We comprehend the desire of expectant parents to take every precaution to ensure the health and welfare of their unborn child. Cord blood banking is one choice that has grown in popularity recently. The two methods of cord blood banking, their distinctions, and potential advantages and disadvantages of each will all be covered in this tutorial.
What is cord blood banking?
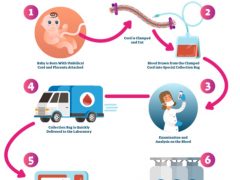
Cord blood banking is the process of obtaining and preserving stem cells from a newborn baby’s umbilical cord blood. Future medical advances could make use of these stem cells to treat a range of illnesses.
Public and private blood banking are the two different types. While public cord blood banks preserve the cord blood for use by anybody in need, private cord blood banks store the cord blood for the child’s or a family member’s personal use.
Private Cord Blood Banking
Parents can store their baby’s cord blood for future use through private blood banking. Depending on the bank and the length of storage, private cord blood banking can cost anywhere from a few thousand to over $10,000.
The promise that the cord blood banked will be accessible for personal use is one advantage of private cord blood storage. Since the preserved cord blood may one day be utilized to treat specific medical conditions, this can be especially significant for families that have a history of certain illnesses.
Yet, there are several disadvantages to private cord blood banking. One worry is that the cord blood that has been kept might not match the infant or other members of the family, rendering it useless. Also, since many of the ailments that can be treated with cord blood stem cells are uncommon, there is a low likelihood of employing the preserved cord blood.
Public Cord Blood Banking
Donating cord blood to a public bank so that it can be utilized by anybody in need is known as public cord blood banking. Since the bank pays for the costs of collection and storage, public blood banking is often free for the donating family.

The fact that donated cord blood is made available to anyone in need and may even save lives is one advantage of public blood banking. Also, because donated cord blood can be utilized by anybody who is a match, the likelihood of using it is higher than with private banking.
There are certain disadvantages to public cord blood banking, though. Since it might already be being used by someone else, the donated cord blood might not be available when needed. Furthermore, there is no assurance that the donor or their family members will match the cord blood supplied.
Conclusion
For families looking to protect their child’s health and wellbeing, cord blood banking can be an invaluable resource. The choice ultimately boils down to personal desire and specific circumstances, however both private and public cord blood banking have advantages and disadvantages.
At our facility, we work hard to give expectant parents the knowledge and tools they need to decide on their child’s health in an informed manner. We hope that this guide has been a useful resource for people thinking about banking cord blood.